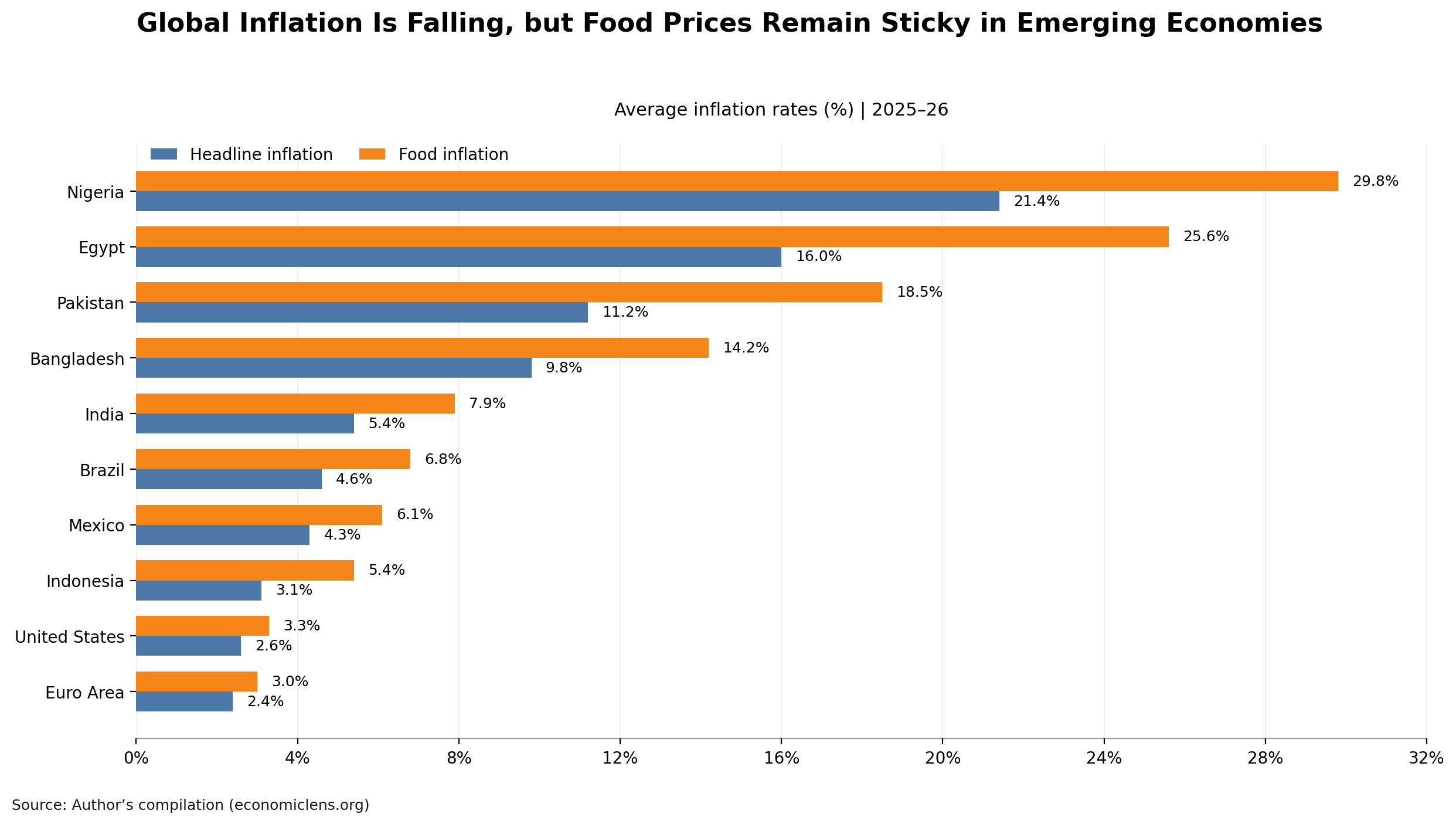
Arctic Resource Power Shift and the Battle for the Future
The Arctic resource power shift is reshaping the global geopolitical landscape. What was once a frozen and remote region is now becoming a strategic prize, and this transformation is accelerating. Because climate change is melting polar ice, new resources and sea routes are rapidly emerging. As a result, polar resource